Musk's Neuralink eyes more test subjects for its brain tech

Elon Musk on Wednesday said his Neuralink startup is "moving on" to a second test patient as its tech for linking brains and computers improves.
Musk and members of the Neuralink team fielded questions during an update streamed on X, formerly Twitter, discussing where it is on the path to making its brain implants commonplace.
"We're only just moving now to our second Neuralink patient," Musk said. "But we hope to have, if things go well, high single digits this year."
Musk's neurotechnology company in January installed a brain implant in Noland Arbaugh, which the billionaire head of Tesla and X touted as a success.
Arbaugh was left paralyzed from the shoulders down by a diving accident eight years ago.
Since the implant operation, he has told of playing chess and the video game "Civilization," as well as taking Japanese and French lessons by controlling a computer screen cursor with his brain.
Musk and members of the Neuralink team detailed fixing an issue that saw Arbaugh's ability to move a computer cursor with his mind greatly reduced.
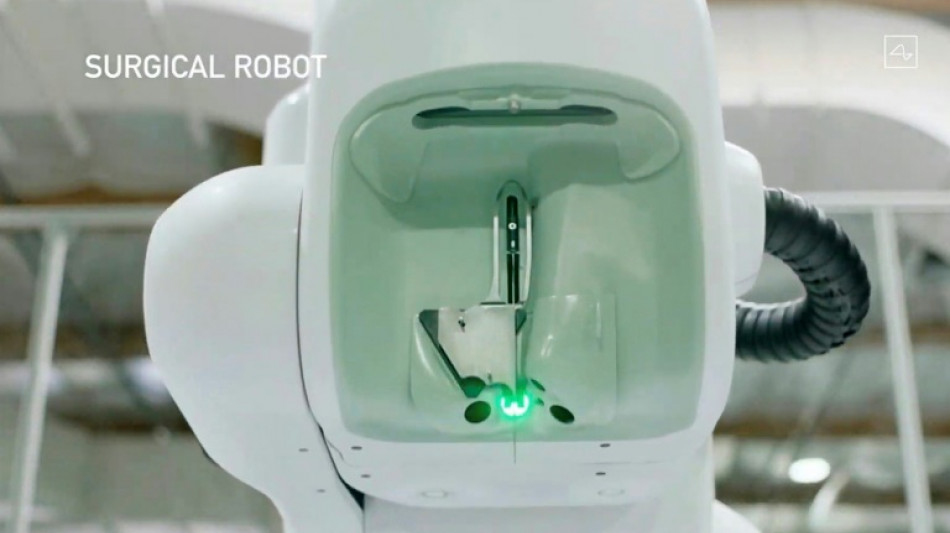
Neuralink's technology works through a device about the size of five stacked coins that is placed inside the human brain by a robotic surgeon.
Threads connecting the implant to Arbaugh's brain had "retracted," becoming less effective at picking up signals.
Threads will be implanted deeper in the brain and at varying depths, with ramped-up precision to maximize effectiveness, according to the Neuralink team.
Musk promised "it's only going to get better from here."
One goal is to escalate the bandwidth of the link between the brain and computer, allowing more data to move faster, according to Musk.
"Quite important for human-AI symbiosis is just being able to communicate at a speed AI can follow," Musk said of brains being connected to computers with artificial intelligence.
Musk envisions Neuralink implants going beyond restoring sight to the blind to giving people infrared or ultraviolet vision or letting them share concepts with others telepathically.
"We want to give people superpowers," Musk said. "Not just that we're restoring your prior functionality, but that you actually have functionality far greater than a normal human."
Musk spoke of developing an automated process in which Neuralink's surgery robot could quickly install custom implants in people seeking "upgrades."
"It's very sort of 'Cyberpunk' or 'Deus Ex,' if you play those games," Musk said of the idea.
"An exciting possibility long term also is to take parts of the Optimus humanoid robot and combine that with a Neuralink - you could have basically cybernetic superpowers," he said.
Musk cofounded Neuralink in 2016.
The ambition is to supercharge human capabilities, treat neurological disorders like ALS or Parkinson's, and maybe one day achieve a symbiotic relationship between humans and AI.
Musk is not alone in trying to make advances in the field, which is officially known as brain-machine or brain-computer interface research.
F.Dodaro--PV
